Last Updated on April 11, 2024 by Chin Yi Xuan
Dividends offer a great way to build passive income from investing. Given time and the compounding effect, dividends can grow exponentially.
In this post, let me go through the key dividend-related terms/jargon!
p
Table of Contents
#1 Dividend
Dividends are essentially a way that companies distribute their earnings to their shareholders.
By doing so, dividend creates a way for shareholders to receive income from their investments. In other words, as an investor, you receive a profit split from the company that you invest in via dividends.
That said, it is not compulsory for most companies to pay dividends.
Certain companies, especially growth-focused companies (eg. Tesla) may prefer to re-invest the profits to grow the business rather than paying them out to investors as dividends.
For consistent dividends, investors may look for stocks and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) with a consistent dividend payout history, or dividend-focused Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs).
#2 Dividend yield (DY)
Dividend yield is an expression of dividends in the form of percentage (%), relative to the share price.
The calculation for dividend yield is as below:
Dividend Yield = (Annual Distribution Per Unit (DPU)/Price) x 100
Example calculation for dividend yield:
Company A pays a total DPU of $0.10 for 2022. Company A’s share price is $1.00 per unit.
As such, the dividend yield is 10%. [($0.1/$1) x 100]
Important:
Avoid investing in a company just because of its high dividend yield! Since DY is formulated by DPU divided by Price, a high DY may be due to a high DPU (generally good), and/or a drop in share price (mostly a bad thing).
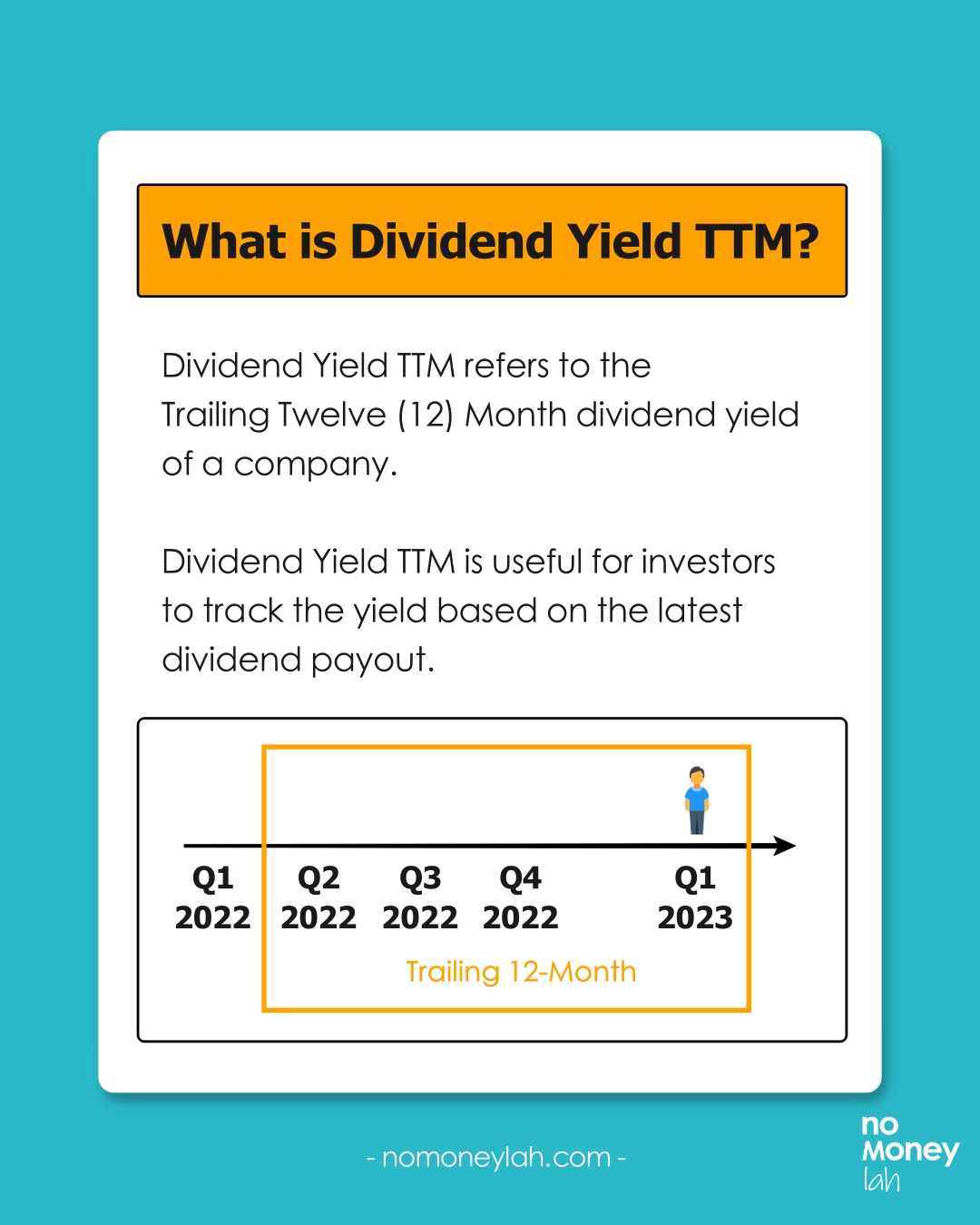
#3 Dividend yield TTM
Dividend yield TTM refers to the Trailing Twelve (12) Months’ dividend yield of a company.
Dividend TTM is useful for investors to track the yield based on the latest dividend payout.
#4 Distribution per unit (DPU)/Distribution per share (DPS)
DPU, or DPS refers to the dividend paid per unit of share.
So, let’s say you have 100 units of Apple shares and Apple distributes a DPU of $0.1/unit. How much in dividends will you get?
The answer is $10 (100 units x $0.1).
#5 Yield on cost
Yield on cost is the dividend you get from your investment, divided by the original cost of the investment.
Yield on cost = (Annual DPU/Cost of investment) x 100
As an example, you bought 100 units of Apple shares at $100/unit. Now, the share price is $150/unit and has a DPU of $5.
- What’s the dividend yield? The dividend yield would be 3.33% ($5 dividend divided by the current $150/unit price).
- How about your yield on cost? In this case, the yield on cost would be $5 DPU divided by your original cost of $100/unit, 5% [($5/$100) x 100].
What if you bought additional shares in between?
Let’s say you bought another 100 units of shares at $120/unit, your cost basis would be:
- ((100 shares x $100) + (100 shares x $120))/200 shares = $110/unit (new cost basis)
Hence, the new yield on cost would be $5 divided by $110, or 4.55% [($5/$110) x 100].
#6 Dividend growth rate (DGR)
Dividend growth rate (DGR) refers to the growth in a dividend payout of a company over a period of time.
Let’s say Company X pays a DPU of $2 in 2021 and $3 in 2022. The DGR would be 50%. (($3 – $2)/$2) x 100).
What if you want to calculate DGR over multiple years (eg. 2018 to 2022)?
| Year | DPU | DGR |
| 2018 | $1.00 | – |
| 2019 | $1.20 | 20% |
| 2020 | $1.70 | 41.7% |
| 2021 | $2.00 | 17.6% |
| 2022 | $3.00 | 50% |
From the table above, there are 2 ways to calculate DGR from 2018 to 2022:
Method 1: Arithmetic Mean DGR
Arithmetic Mean DGR = (DGR1 + DGR2 + DGR3…+DGRn)/n
Arithmetic Mean DGR from 2018 to 2022: (20% + 41.7% + 17.6% + 50%)/4 = 32.33%
*n = Number of periods where dividend growth rates are provided
Method 2: Compounded DGR
Compounded DGR = [((DPUn/DPU0)^(1/n))-1] x 100
Compounded DGR from 2018 – 2022: [(($3/$1)^(1/5))-1] x 100 = 24.57%
*n = Number of years
#7 Dividend growth streak
Dividend growth streak refers to the continuous period where a company/ETF increases its dividend payout.
From the DGR example in the previous section, Company X has a 4-year dividend growth streak from 2018 – 2022.
#8 Dividend payout frequency
Dividend payout frequency indicates how many times a company/ETF pays out dividends in a year.
Out of all options, a quarterly payout (ie. 4x per year) is the most commonly seen payout policy.
However, there are companies/ETFs that adopt monthly and semi-annual payouts as well.
#9 Payout ratio (%)
Payout ratio measures the proportion of earnings a company pays to its shareholders as dividends.
Generally, a low payout ratio would mean the company is reinvesting its earnings to grow the business.
That said, it is common to see dividend stocks having a 40 – 60% payout ratio, while most REITs are required to pay out at least 90% of their profits to investors.
Important:
A payout ratio over 100% may indicate an unsustainable payout practice as it is paying more than it is earning.
#10 Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP/DRP)
A Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP or DRP) is a program that allows investors to reinvest their dividends into additional shares automatically.
DRIP is a great (and important) tool for investors to automate their dividend compounding process.
If you want to learn about DRIP, check out my detailed walkthrough + example calculations below!
READ MORE: Introduction to Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRP) + Example Calculation
#11 Dividend withholding tax (WHT)
Dividend withholding tax (WHT) is a method whereby a country’s government collects taxes from non-residents who have derived dividend income from the country.
Dividend WHT is deducted from the dividends before it is distributed to investors.
If you are a dividend investor, dividend WHT is a MUST-KNOW! Learn about Dividend WHT as a Malaysian investor HERE.
READ MORE: All you need to know about Dividend Withholding Tax (WHT)
#12 Dividend ex-date
Dividend ex-date refers to the day on which you have to hold on to a company’s shares in order to be eligible for their announced dividend.
Example: Apple announces a dividend payout with a dividend ex-date of 1/1/2023.
In this case, to be eligible to receive the dividend, an investor will need to hold his/her shares until 1/1/2023.
#13 Dividend payout date
Dividend payout date is the day your dividends will be paid out to you (either via your brokerage account or bank account, depending on your brokers).
#14 Special dividends
A special dividend is usually a one-off dividend that is paid to investors when a company finds that it has excess cash.
Most of the time, this is due to a special occasion like the divestment of a property, which puts a company in the state of additional cash holdings.
No Money Lah Verdict
I hope this guide has been clear and helpful!
If you have any questions on dividend investing, or the jargon/terms involved, feel free to let me know in the comments section below!
Looking for a reliable global broker? ProsperUs has you covered!
This educational post is sponsored by ProsperUs by CGS-CIMB.
ProsperUs by CGS-CIMB is a regulated broker from Singapore that gives investors access to 30+ exchanges in more than 8 countries. (US, Hong Kong, China, Japan, UK, Singapore, Malaysia, Europe, and more!)
Now that you’ve learned about dividend withholding tax, you have the choice to invest in countries with a more efficient tax rule via ProsperUs!
In addition, ProsperUs offers multiple instruments from stocks, ETFs, futures, options, Forex, and CFDs. This is great for investors looking to diversify across different asset classes.
Exclusive ProsperUs Referral Code – MONEY20
If you are thinking to give ProsperUs a try, here’s something exclusive to No Money Lah readers – you will not find this anywhere else!
From today till 30/6/2024, key in my exclusive promo code ‘MONEY20’ while you register, and get FREE cash credits up to SGD100 when you open a ProsperUs account:
p
| Tier | Initial funding within 30 days of account set up | Trades Executed | Cash Credits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Minimum SGD500 – SGD2,999 | Minimum 3 trades executed | SGD10 |
| 2 | Minimum SGD3,000 – SGD14,999 | Minimum 3 trades executed | SGD20 (Deposit SGD3000 or more), OR SGD20 + SGD30 (Deposit SGD3000 or more + Min. trades fulfilled) |
| 3 | SGD15,000 or more | Minimum 3 trades executed | SGD20 (Deposit SGD3000 or more), OR SGD20 + SGD100 (Deposit SGD15,000 or more + Min. trades fulfilled) |
Click HERE to view the full T&C of this referral reward.
Open a ProsperUs Account Today!
Disclaimers
This article is brought to you in collaboration with ProsperUs by CGS-CIMB.
Any of the information above is produced with my own best effort and research.
This post is produced purely for sharing purposes and should not be taken as a buy/sell recommendation. Past return is not indicative of future performance. Please seek advice from a licensed financial planner before making any financial decisions.
This post may contain promo code(s) that afford No Money Lah a small amount of commission (and help support the blog) should you sign up through my referral link.
Related Posts
Subscribe to No Money Lah's Newsletter!
Get FREE updates to tips & ideas to live a better and more fulfilling financial life :)
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Chin Yi Xuan
Hi there! I am Yi Xuan. I am a writer, personal finance & REIT enthusiast, and a developing trader with the goal to become a full-time funded trader. Every week, I write about my personal learnings & discovery about life, money, and the market.