Last Updated on May 2, 2022 by Chin Yi Xuan
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are essentially companies that operate and/or manage real estates. REITs are especially well-received among long-term investors that are looking for a reliable passive income stream.
To invest in REITs is identical to typical stock investment – you buy their shares through your stock broker.
That said, here are 5 terminologies that you HAVE TO know before investing in REITs:
Table of Contents
(1) Distribution/Distribution Per Unit (DPU)
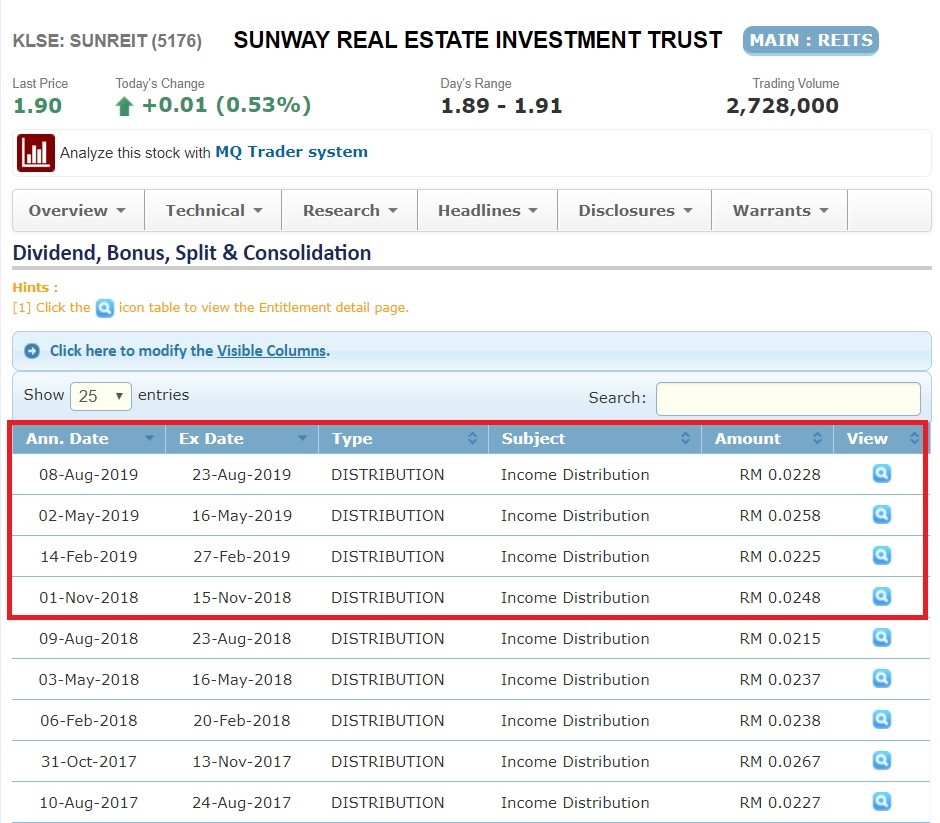
Distribution is one of the MOST IMPORTANT elements in REIT investing. Essentially, distribution refers to the total amount of money that a REIT is paying back to its investors at the end of every quarter or Financial Year (FY).
As such, take the total distribution of a REIT and divide by the total number of shares of a REIT, and you will get the Distribution Per Unit – a.k.a. the total amount of distribution you will get as one unitholder of a share in the particular REIT.
p
(2) Dividend Yield
Compared to Distribution/Distribution Per Unit, Dividend Yield is much more familiar to people.
In short, Dividend Yield is derived from Distribution Per Unit (DPU) – by dividing DPU with the price per unit of a REIT.
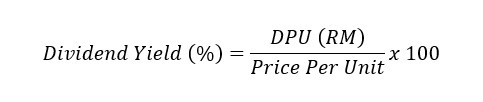
From the example above, the Dividend Yield of SunREIT for its latest four quarters is:

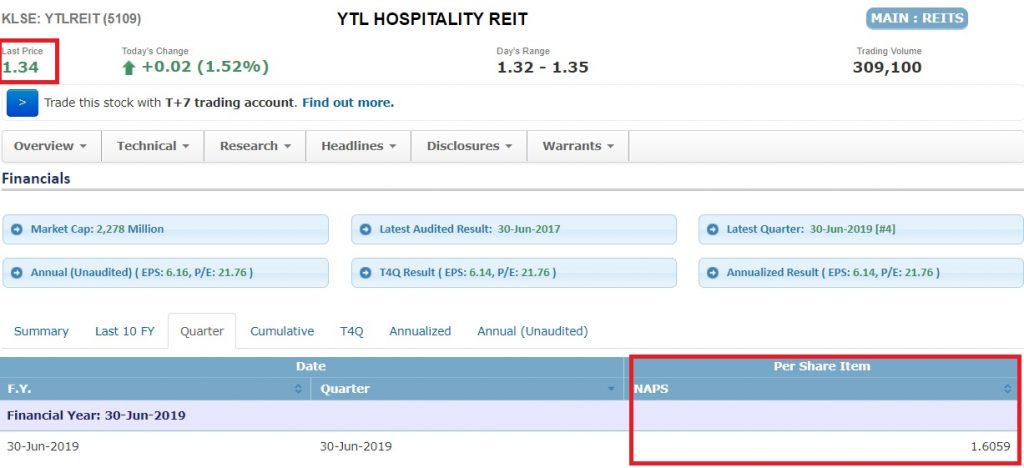
(3) Net Asset Value (NAV)/Net Asset Value Per Unit (NAVPU)
Net Asset Value shows the total worth of the net assets of a REIT.
When divided by the total shares (or units issued) of a REIT, you will get the value of Net Asset Value Per Unit (NAVPU), a.k.a. the total value of the net asset of a REIT per share.
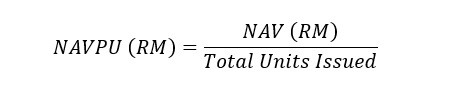
NAVPU is very useful to determine if a REIT is undervalued or overvalued. As an example, if the price of a REIT is less than NAVPU, it shows that a REIT is currently market-priced at a value less than the worth of the net asset of the REIT (undervalued).
p
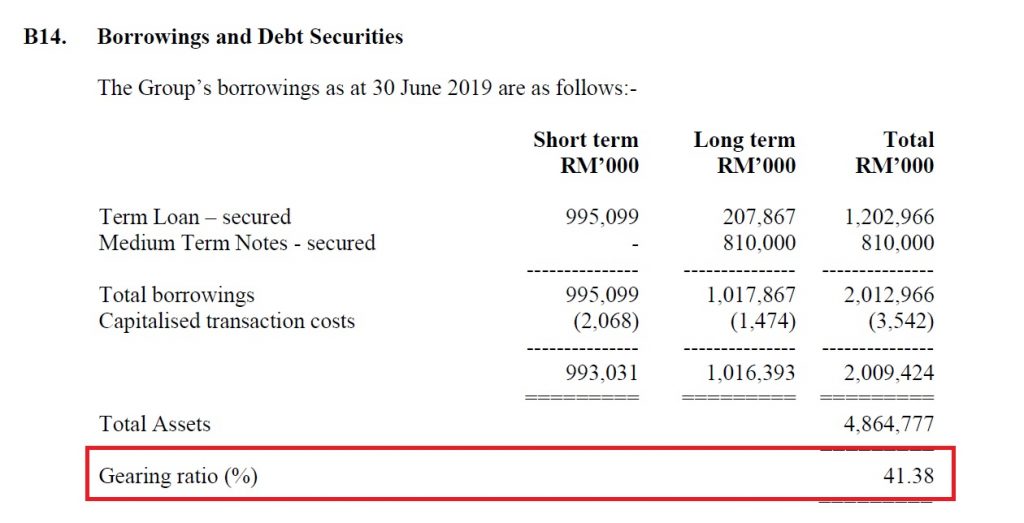
(4) Gearing
Gearing refers to the leverage of a REIT. Essentially, it refers to how much is the total debt of a REIT in relative to its total asset.
Generally, a REIT is legally required to maintain a Gearing of 50% or less.
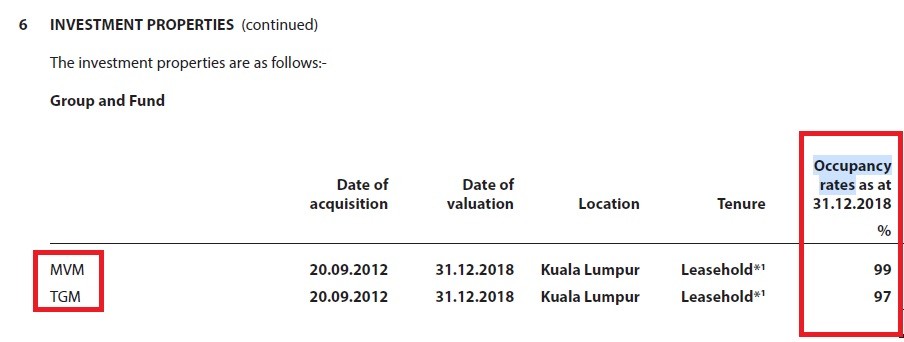
(5) Occupancy Rate
Occupancy rate is extremely crucial to determine if a REIT is going to earn money. Simply put, the more tenants that occupy a REIT’s property, the higher the occupancy rate of the property.
Generally, we should want to look for REITs that have a high occupancy rate for their real estate portfolio:
No Money Lah’s Verdict:
So that’s it! Here are 5 terminologies that you MUST KNOW while investing in REITs. While this is a short and simple article, yet if you are new to REITs, I definitely hope that you find this article informative!
If you find this article useful, do share this article out to benefit more people around you! Also, do check out my articles on WHY you should invest in REITs, and the different TYPES of REITs in the market (and why they matter!)
Related Posts
Subscribe to No Money Lah's Newsletter!
Get FREE updates to tips & ideas to live a better and more fulfilling financial life :)
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Chin Yi Xuan
Hi there! I am Yi Xuan. I am a writer, personal finance & REIT enthusiast, and a developing trader with the goal to become a full-time funded trader. Every week, I write about my personal learnings & discovery about life, money, and the market.




Hi Yi Xuan, I’m super new in this investment journey and I tend to get confuse with terms frequently. By saying that, this article is very helpful for me. It would be great if you could explain differences between (NAVPU) and price to book ratio as they seems similar to me. Thanks in advance.
Hi Sharm!
Thanks for your comment and glad that this article is benefitting you!
NAVPU essentially tells us about the general fair value of a share by taking its NET Asset Value (ie. assets – liabilities) and divide the number by the share price.
P/B ratio is in short, taking the price of a share divided by the book value of a company. The Book Value can be understood (and calculated) as Net Asset BUT it can also be calculated by taking the sum total of the overall Shareholder Equity of the company.
The difference in usage is essentially NAVPU can be used individually vs the share price to determine if a company is undervalued or not (eg. A REIT is undervalued if the share price is RM1.00 and the NAVPU is RM1.50), while P/B ratio of a company needs to be used in RELATIVE to other company’s P/B ratio to see if it is undervalued or not.
Hope this helps!
Yi Xuan
Thanks for sharing Yi Xuan!
Some REITS have dividend yield of way above 5 – 7 %. Is that a warning sign?
Hi Ken,
Happy to share!
For your question, I’d say it depends.
A yield could be high because:
1. The company is doing well and it pays out more dividends to investors, or;
2. The share price is dropping and hence making the dividends seem more attractive than it actually is.
You gotta find out what led to the high yield. (1) is generally good and (2) is most likely a no-no.
Hopefully this helps!
Yi Xuan